Theme: A Lifesaving Mission to end Cancer Forever
Cancer Targets 2019
Cancer Targets 2019 welcomes all the attendees, speakers, sponsor’s and other research expertise from all over the world to the "International Conference on Biomarkers and Cancer Targets" which is going to be held during February 14-15, 2019 in Dubai, UAE. We are very much honoured to invite you all to exchange and share your views and experience on the “A Lifesaving Mission to end Cancer Forever”.
The unique international on biomarker and cancer target conference 2019 directs towards addressing main issues as well as future strategies s of cancer. This is going to be the largest and most promising international conference where the researcher as well as decision makers will come to discuss and debate on various aspects of the challenges, risks and investment opportunities throughout the complete information of cancers. The program includes the complete information of cancers including cancer target therapy, Cancer nursing and care, Economic impact on cancer, Biomarker and advance use of biomarkers, the entire medical team involved in patient care, researcher, Professional, early career individuals and patient advocates who wish to learn principles of tumour immunology and immunotherapy.
ME Conferences organizes 3000+ Global events in conference series every year across the globe with support from 1000+ more scientific societies and Publishes 700 open access journals which contains over 100000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Who attends:
With members from around the world focused on learning about biomarkers and cancer biomarkers, and its advances; this is your best opportunity to reach the largest assemblage of participants from the biomarker community. Participants can conduct presentations, distribute information, meet with current and potential scientists, make a splash with new drug developments, and receive name recognition at this 2-day event. World-renowned speakers, the most recent techniques, developments, and the newest updates in and cancer biomarkers are hallmarks of this conference.
Target Audience:
- Oncologists
- Pathologists
- Hematologists
- Immunologists
- Clinical Researchers
- Nursing
- Cancer Researchers
- Scientists
- Young Researchers
- Students
- Biomarker Associations and Societies
- Business Entrepreneurs
- Training Institutes
- Software developing companies
- Manufacturing Medical Devices Companies
- Data Management Companies
- Pharmaceutical Companies
- Diagnostics Companies
Track 1: Cancer Biomarkers
Cancer biomarkers can be DNA, mRNA, proteins, metabolites, or processes such as apoptosis, angiogenesis or proliferation. The markers are produced either by the tumor itself or by other tissues, in response to the presence of cancer or other associated conditions, such as inflammation. Such biomarkers can be found in a variety of fluids, tissues and cell lines. "A biological molecule found in blood, other body fluids, or tissues that is a sign of a normal or abnormal process, or of a condition or disease. A biomarker may be used to see how well the body responds to a treatment for a disease or condition. It is also called as molecular marker and signature molecule.
Track 2: Cancer Molecular Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy is the foundation of precision medicine. It is a type of cancer treatment that targets the changes in cancer cells that help them grow, divide, and spread. As researchers learn more about the cell changes that drive cancer, they are better able to design promising therapies that target these changes or block their effects. In cancer, a type of treatment that uses drugs or other substances to target specific molecules involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells. Blocking these molecules may kill cancer cells or may keep cancer cells from growing or spreading. Molecularly targeted therapy may cause less harm to normal cells and may have fewer side effects than other types of cancer treatment.
Track 3: Cancer Proteomics
Proteomics advancements are utilized for early discovery and finding of diseases for the improvement of novel restorative operators. Distinguishing proof of biomarker and furthermore the investigation of protein articulation of the disease are examined through proteomics stages. These investigations have prompted the advancement of finding new medications and focused on therapeutics towards the tumour cells. Identification, anticipation, finding and treatment of breast malignancy is presently conceivable with the headways in the field of proteomics alongside the utilization of mass spectrometry. The disclosure of the protein designs has empowered scientists to recognize the disease and disease free-state related with breast disease has been revealed with the improvement of proteomics advancements. This revelation prompts customized treatment for the patients. Proteins communicated or found in the serum, plasma and the tumour cells utilizing the novel procedures give a superior perspective of the heterogeneity of the diseases.
Track 4: Cancer Epigenetics
Cancer epigenetics is the investigation of epigenetic alterations to the DNA of malignancy cells that don't include an adjustment in the nucleotide arrangement. Epigenetic changes might be similarly as vital, or much more critical, than hereditary changes in a cell's change to malignancy. A variety of compounds are considered as epigenetic carcinogens such as arsenite, diethylstilbestrol, hexachlorobenzene and nickel compounds. They result in an increased incidence of tumors, but they do not show mutagen activity.
Track 5: Biomarker Testing
Biomarker testing is at the centre of personalized medicine. The word "biomarker" refers to any of your body's molecules that can be measured to assess your health. Molecules can be obtained from your blood, body fluids, or tissue. Biomarker testing is a group of tests that looks for these molecular signs of health so that doctors can plan the best care. Biomarker testing may also be called "molecular testing" or "genetic testing" Biomarker tests can be divided into three groups: chromosome, gene, and biochemical. Each of these groups is described below. In addition, examples of each type of test are given.
Track 6: Cancer Prognosis and Predictive Factor
A prognostic factor is an element of the malignancy (like the extent of the tumour) or a normal for the individual (like their age) that may influence the result. A predictive factor can help foresee if a malignancy will react to a specific treatment. A few medications just work if atoms, (for example, proteins) are on growth cells or inside them. These are some essential prognostic elements identified with the tumour: The sort of disease, The subtype of malignancy in light of the sort of cells or tissue (histology), The extent of the tumour, How far and where the malignancy has spread, How quick the malignancy cells are developing. Important predictive elements incorporate a few sorts of tumour markers, biomarkers and changes to chromosomes (hereditary transformations).
Track 7: Cancer Epidemiology
Cancer Molecular epidemiology is a branch of oncology and epidemiology that focuses on the contribution of potential environmental and genetic risk factors, identified at the molecular level, to the etiology, distribution and prevention of cancer within families and across populations. The goal of molecular epidemiology is to supplement and integrate existing methods. Molecular epidemiology of cancer studies molecular markers of distribution of malignant tumours in the population and their effects on individual risk of developing a disease. Molecular markers can be detected in tissues and biological liquids and characterize individual exposure to carcinogens, biological effect of the exposure, genetic susceptibility to the development of disease, and final result of carcinogenesis. Identification of specific somatic molecular and genetic changes, so-called fingerprints, is very important for the molecular characteristics of a tumour and confirmation of etiology.
Track 8: Pathophysiology of Cancer
Pathophysiology of cancer incorporates reason for the sickness, conclusion, how the infection creates, instrument and characteristic course of the illness. They additionally manage biochemical highlights, movement, and guess or result of the ailment. Pathology of tumours and other complex issue have experienced an ocean change after improvement of innovations like immunohistochemistry, stream cytometry, and sub-atomic biologic ways to deal with malignancy analysis.
Track 9: Cancer Diagnosis, Nursing & Care
With advances in technologies that understand cancers better, there is a rise of number of diagnostic tools that can help detect cancers. Once suspected, diagnosis is usually made by pathologists and oncopathologists and imaging radiologists. Diagnostic testing involves tests and procedures to confirm the presence of disease and identify the correct tumor type, location, extent and stage.
Authority medical attendants, ward medical care takers, Community medical care takers, Specialist palliative care medical attendants, Marie Curie Cancer Care Nurses are some of the various type of nurse cares available for the cancer treatment. Authority attendants work primarily in doctor's facilities, however some give mind in the patient's home. They may have some expertise in a particular malignancy for instance bosom, lung, head and neck disease, or a specific treatment, for instance chemotherapy. Community attendants give an extensive variety of nursing care including helping patients when they leave clinic, taking out fastens, wiping wounds and giving out some prescription at home. Authority palliative care medical care takers have skill in overseeing torment and different manifestations, and can offer help for individuals with growth and their families. Marie Curie medical caretakers give hands on mind at home during that time or night, offering the carer a reprieve. They will have exceptional learning of palliative care.
Track 10: Cancer Biopsy
The expulsion of cells or tissues for examination by a pathologist. The pathologist may ponder the tissue under a magnifying lens or perform different tests on the cells or tissue. There are a wide range of sorts of biopsy techniques. The most widely recognized sorts include: (1) incisional biopsy, in which just an example of tissue is evacuated; (2) excisional biopsy, in which a whole irregularity or suspicious zone is expelled; and (3) needle biopsy, in which a specimen of tissue or liquid is expelled with a needle. At the point when a wide needle is utilized, the strategy is known as a centre biopsy. At the point when a thin needle is utilized, the methodology is known as a fine-needle goal biopsy.
Track 11: Cancer Pharmacology
Cancer pharmacology incorporate investigations of the fundamental mechanism of signal transduction related with cell multiplication and apoptosis, the mechanism of activity of anti-neoplastic specialists, the outline and revelation of new medications, essential components of DNA repair and DNA harm resilience and the advancement of novel techniques for quality treatment.
Track 12: Biomarkers in Medicine
In medicine, a biomarker is a measurable indicator of the severity or presence of some disease state. More generally a biomarker is anything that can be used as an indicator of a particular disease state or some other physiological state of an organism. A biomarker can be a substance that is introduced into an organism as a means to examine organ function or other aspects of health. More specifically, a biomarker indicates a change in expression or state of a protein that correlates with the risk or progression of a disease, or with the susceptibility of the disease to a given treatment. Biomarkers can be characteristic biological properties or molecules that can be detected and measured in parts of the body like the blood or tissue. Biomarkers can be specific cells, molecules, or genes, gene products, enzymes, or hormones. Complex organ functions or general characteristic changes in biological structures can also serve as biomarkers. Although the term biomarker is relatively new, biomarkers have been used in pre-clinical research and clinical diagnosis for a considerable time.
Track 13: Factors Associated with Cancer Prevalence
The association between cancer prevalence and race, income, insurance, and education was estimated using the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey data from 1996-2007. The goal of this analysis was to provide some insight into how variations in race and socioeconomic factors influence the prevalence of cancer. This analysis was conducted for any cancer and for the four most common cancer sites i.e. lung, colorectal, breast and prostate. Initially, the model was estimated using MEPS data from 2002-2007 to include body mass index, exercise and smoking behaviour as predictors in the model. This data is not available in the MEPS for the prior years. We compared the results of our model with and without these variables and concluded that they did not confound the associations between cancer prevalence and race, income, insurance, and education. Therefore, we dropped these variables from the analysis and were able to expand our data to include the years 1996-2001. This increased the number of persons with cancer in our analysis and was important for our analysis of the four most common cancer sites.
Track 14: Economic Impact on Cancer targets
The financial costs of cancer are high for both the person with cancer and for society as a whole. The Agency for Healthcare research and Quality (AHRQ) estimates that the direct medical costs (total of all health care costs) for cancer in the US in 2014 were $87.8 billion.58% of this cost is for hospital outpatient or doctor office visits, 27% of this cost is for inpatient hospital stays. These estimates are based on a set of large-scale surveys of individuals and their medical providers called the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS). One of the major costs of cancer is cancer treatment. But lack of health insurance and other barriers to health care prevent many Americans from getting optimal health care. According to the US Census Bureau, about 29 million people (9%) in the US were uninsured in 2015.The percentage of uninsured ranged from 3% in Massachusetts to 17% in Texas.
Track 15: Types of Cancer Biomarkers
A Biomarker is the organic particle found in blood, other body liquids, or tissues that is an indication of a typical or anomalous process, or of a condition or disease. A biomarker might be utilized to perceive how well the body reacts to a treatment for a malady or condition. Cancer biomarkers are arranged by their diverse capacities: Biomarkers that Trigger Cells to Grow and Multiply Abnormally, Biomarkers That Support a Treatment's Cellular or Molecular Action, Biomarkers That Disrupt a Treatment's Cellular or Molecular Action, Detecting and Measuring Biomarkers to Develop a Personalized Anticancer Treatment Plan.
Tracks 16: Cancer Types – Targets & Therapy
Targeted cancer therapies are drugs or targeting specific genes or proteins which are found in cancer cells or in cells related to cancer growth, like blood vessel cells that block the growth and spread of cancer by interfering with specific molecules that are involved in the growth, progression, and spread of cancer. Molecularly targeted drugs or molecularly targeted therapies are sometimes come under Targeted cancer therapies. Many different targeted therapy types for cancer treatment are in available which are as follows.
Some targeted therapies like Cancer vaccines and gene therapy interfere with the growth of specific cancer cells are considered under targeted therapies. A candidate is determined whether a patient is for targeted therapy will have an appropriate target for a particular targeted therapy and will be treated. In case of CML: most patients have the BCR-ABL fusion gene and for other cancer types a patient’s tumor tissue must be tested to determine target is present or not. The use of a targeted therapy will be restricted to patients whose tumor has a specific gene mutation that codes for the target; patients who do not have the mutation will not be targeted.
Scope and Importance:
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body. Cancerous cells are also called malignant cells. Cancer grows out of cells in the body. Normal cells multiply when the body needs them, and die when they are damaged or the body doesn't need them. Cancer appears to occur when the genetic material of a cell becomes changed. This results in cells growing out of control. Cells divide too quickly and do not die in a normal way. Some cancers are more common in certain parts of the world. For example, in Japan, there are many cases of stomach cancer. But in the United States, this type of cancer is less common. Differences in diet or environmental factors may play a role. Cancer affects many people. It is not limited by gender, age, or ethnicity and has no physical barriers within the body. In America alone, as of 2007, 27% of Americans had or were being treated for some form of cancer.
Why it’s in Dubai, UAE?
Cancer target 2018 is going to held in Dubai. Dubai is the largest and most populous city in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). It is located on the southeast coast of the Persian Gulf and is the capital of the Emirate of Dubai, one of the seven emirates that make up the country. Dubai was ranked 44th among the world's best financial cities and the world's 27th richest city in 2012. It is also an international financial center and has been ranked 37th within the top 50 global financial cities and 1st within the Middle East. As indicated by an examination give an account without bounds intensity of urban communities, in 2025, Dubai will have climbed to 23rd place in general in the Index.. Public hospitals in Dubai were first built in the late 1950s and continued to grow with public health initiatives. There are now 28 hospitals in Dubai, 6 public and 22 private, with 3 more major hospitals scheduled to be built by 2025. Tumour examine is basically going ahead in Asian nations close to Dubai, so it is a reasonable goal for Oncology and malignancy gatherings.
Conference Highlights:
-
Cancer Biomarkers
-
Cancer Molecular Targeted Therapy
-
Cancer Proteomics
-
Cancer Epigenetics
-
Biomarker Testing
-
Cancer Prognosis and Predictive Factor
-
Cancer Epidemiology
-
Pathophysiology of Cancer
-
Cancer Diagnosis, Nursing & Care
-
Cancer Biopsy
-
Cancer Pharmacology
-
Biomarkers in Medicine
-
Factors Associated with Cancer Prevalence
-
Economic Impact on Cancer targets
-
Types of Cancer Biomarkers
-
Cancer Types – Targets & Therapy
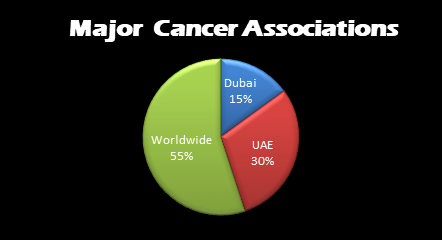
Major Cancer Associations:
In Dubai
- Ernakulam Pravassi Welfare Association
- Ananthapuram Non Residents Association
- Venjaramoodu Non Resident Malayalee
- Dubai Charity Association
- Dubai Chamber Of Commerce & Industry
In UAE
- Emirates Medical Association
- Emirates Society of Haematology
- Dubai Health Authority
- Middle East cancer consortium
Worldwide
- Union for International Cancer Control
- Armenian Association of Haematology & Oncology
- Cancer Association of South Africa
- Canadian Cancer Society
- Society for Paediatric Oncology & Haematology
- Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology
- Cancer Research UK
- Indian Association of blood cancer & Allied Diseases
- The Leukaemia and Lymphoma Society of Canada
- Leukaemia Cancer Society
- Leukaemia & Blood Cancer New Zealand
- Korean Cancer Association
- Leukaemia Foundation of Australia
- Indian Cancer Society
- Brazilian Lymphoma & Leukaemia Association
- Children’s Cancer and Leukaemia Group
- German Cancer Society
- Lymphoma Foundation Canada
- Cancer Society of Finland
- France Lymphoma Hope
- Leukaemia &Blood Cancer, New Zealand
- Medical Oncology Group of Australia
- Childhood Cancer Research Group, UK
- National Cancer Institute of Argentina
- Cancer Society Nepal
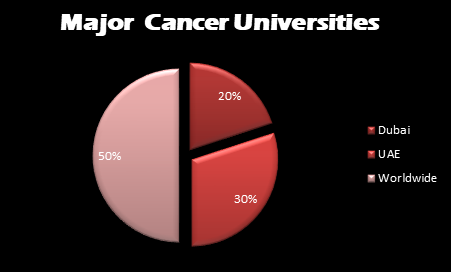
Top Universities:
In Dubai
- Murdoch University, Dubai
- Heriot Watt University Dubai Campus
- Modul University Dubai
- Middlesex University Dubai
- Hamdan Bin Mohammed Smart University
- Curtin University Dubai
- University of South Wales Dubai
- Emirates Aviation University
In UAE
- Al Ghurair University (AGU)
- University of Dubai (UD)
- Zayed University
- American University in Dubai (AUD)
- British University in Dubai (BUiD)
- American University in the Emirates (AUE)
Worldwide
- University of Chicago, Chicago
- University of Toronto, Canada
- Washington University in St. Louis
- University of Tokyo, Japan
- Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, China
- University of Lyon, France
- University Of Queensland, Australia
- University of Arizona Cancer Center
- University of Utah
- University of Pittsburgh
- University Of Florida
- University Of British Columbia
- University of north Durham
- University Of Edinburgh
- University Of Bordeaux, France
- Oregon Health and Science University
- Loyola University Chicago
- University of Louisville
- University Of Western Sydney, Australia
- University of Melbourne
- University Of South Australia
- University Of New South Wales
- University of Milan, Italy
- Kyoto University, Japan
- National Taiwan University
- The University of Manchester, UK
- Pondicherry University, India
- Hackensack University Medical Center
- Kyoto University, Taiwan
- Osaka University, Japan
Related Societies:
American Society of Clinical Oncology, European Society For Medical Oncology, International Agency for Research on Cancer, International Society of Geriatric Oncology, International Society of Paediatric Oncology, European Society of Breast Cancer Specialists, European Society of Surgical Oncology
Other Related Societies:
USA: American Cancer Society, American Childhood Cancer Organisation, American Society for Blood & Marrow Transplantation, American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology, American Society of Clinical Oncology, American Society of Haematology, American Society of Paediatric Oncology ,American Association for Cancer Research, American Brest Cancer Foundation, Hematology/Oncology Pharmacy Association, International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
Europe: European Cancer Organisation, European Cervical Cancer Association , European Head and Neck cancer Awareness, European Hematology Association, European society of molecular imaging, UK Oncology Nursing Society, United Kingdom Association of Cancer Registries, Childhood Cancer Research Group Cancer Focus BASO, European Society of Oncologic Imaging, European Association for Cancer Research, European Society for Medical Oncology, European Society for Medical Oncology, UK Oncology Nursing Children’s Cancer and Leukaemia Group Society, EFB European Federation of Biotechnology, European Diagnostic Manufacturers Association, European Society of Pathology ICGEB, International Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology
Asia Pacific: Chinese Society for Cell Biology (CSCB), Chinese Society of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, The Hong Kong Society of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, The Chinese Biological Investigator Society, Australian Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Chinese Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology , Korean Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (KSBMB), The Federation of Asian and Oceanian Biochemists (FAOB), Japan Society for Molecular Science, The Genetics Society of Japan (GSJ), Fungal Molecular Biology Society of Japan, Association for Molecular Pathology (AMP), Molecular Pathology Association of India (MPAI).
Middle East : Moazzara – Emirates Association for Cancer Support, Angels of Mercy Cancer Society, Friends of Cancer Patients Society, Association for Molecular Pathology, Thailand division of International Academy of Pathology, Taiwan Society of Pathology, Indonesian Association of Clinical Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Romanian Society of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Romanian Society of Human Genomics, The Malaysian Biochemical Society, Malaysian Society for Molecular Biology and Biotechnology
Conference Highlights
- Cancer Biomarkers
- Cancer Types – Targets & Therapy
- Cancer Molecular Targeted Therapy
- Cancer Proteomics
- Cancer Epigenetics
- Biomarker Testing
- Cancer Prognosis and Predictive Factor
- Cancer Epidemiology
- Pathophysiology of Cancer
- Cancer Diagnosis, Nursing & Care
- Cancer Biopsy
- Cancer Pharmacology
- Biomarkers in Medicine
- Factors Associated with Cancer Prevalence
- Economic Impact on Cancer targets
- Types of Cancer Biomarkers
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | October 14-15, 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Molecular Biomarkers & Diagnosis
- Journal of Cancer Science & Therapy
- Journal of Carcinogenesis & Mutagenesis
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by